# KUDO Kafka Access
Kafka is a fully distributed messaging system as it persists, receives and sends records on different brokers.
Which in result makes it easier to scale it horizontally and provides guarantees for an architecture that can be fault tolerant.
To fully take advantage of the Apache Kafka sharding, a typical scenario would be where different producers and consumers are connecting to all Kafka brokers and writing and reading messages from the brokers.
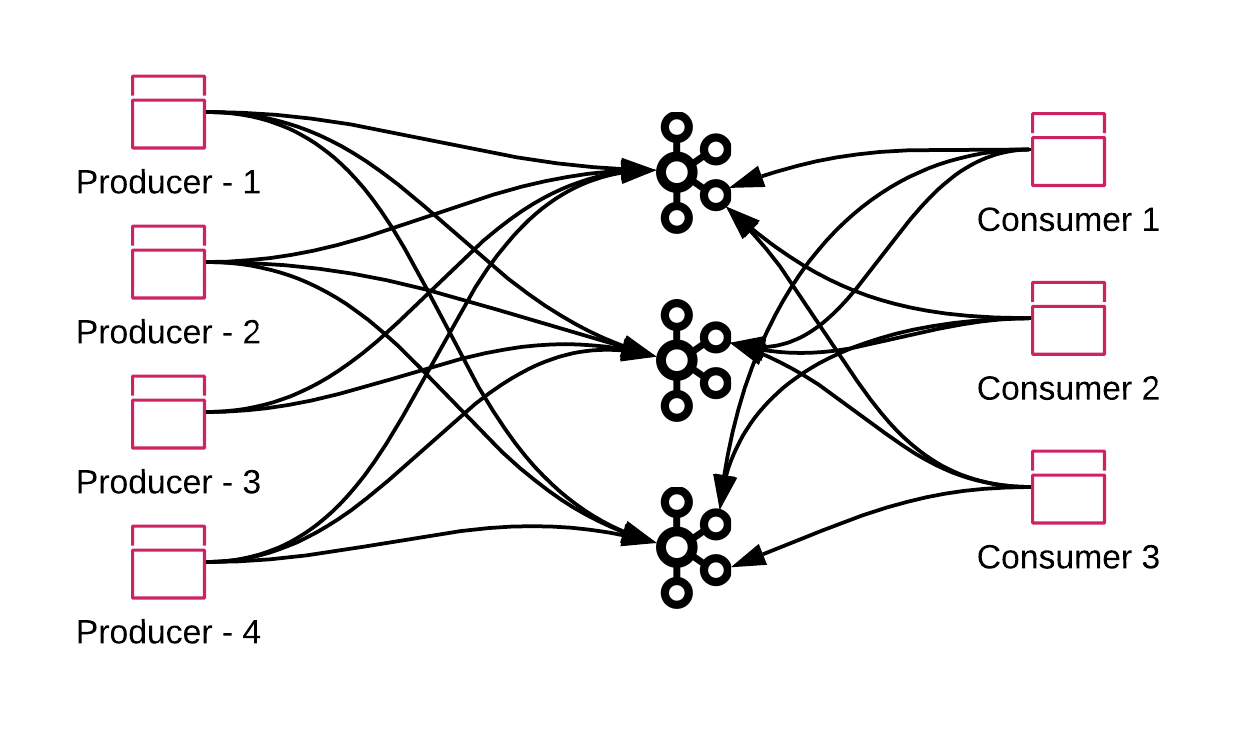
To achieve this, we need to guarantee that the producers and consumers can directly access the brokers from inside and outside of a Kubernetes cluster.
# Internal access
For the applications living inside the same kubernetes cluster. KUDO Kafka supports the headless service.
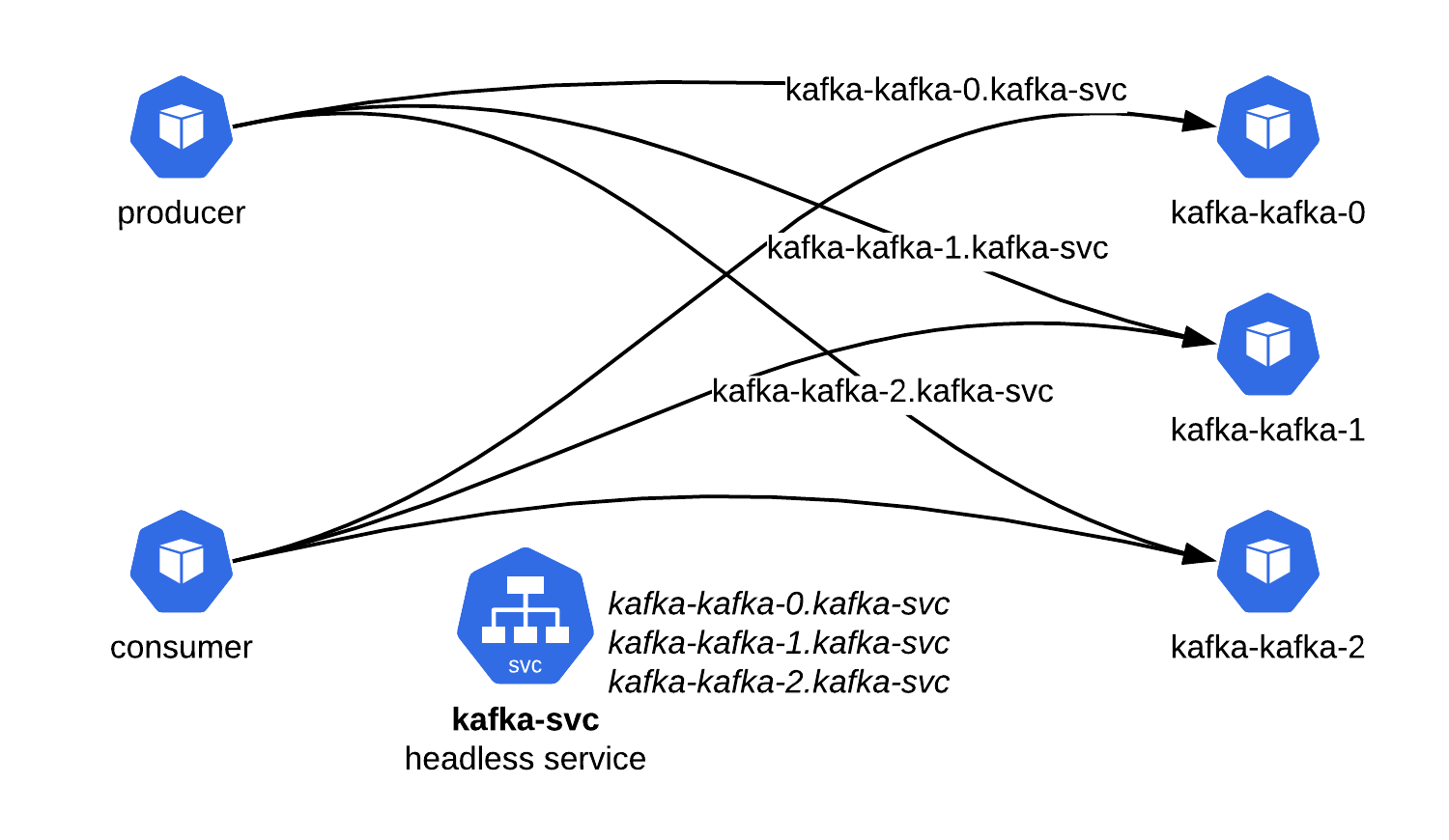
# External access
For the producers and consumers living outside the Kubernetes cluster KUDO Kafka supports the Nodeport and Loadbalancer approach.
# Loadbalancer (recommended)
Exposing the Apache Kafka brokers using the LoadBalancer Service Type is the recommended way for the KUDO Kafka.
KUDO Kafka can be exposed easily for external access using Service Type LoadBalancer (opens new window).
The parameter used to configure the external loadbalancers is EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER_TYPE
When set to LoadBalancer it creates one service per broker to expose each broker externally.
$ kubectl kudo install kafka --instance=kafka-instance \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER=true \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER_TYPE=LoadBalancer
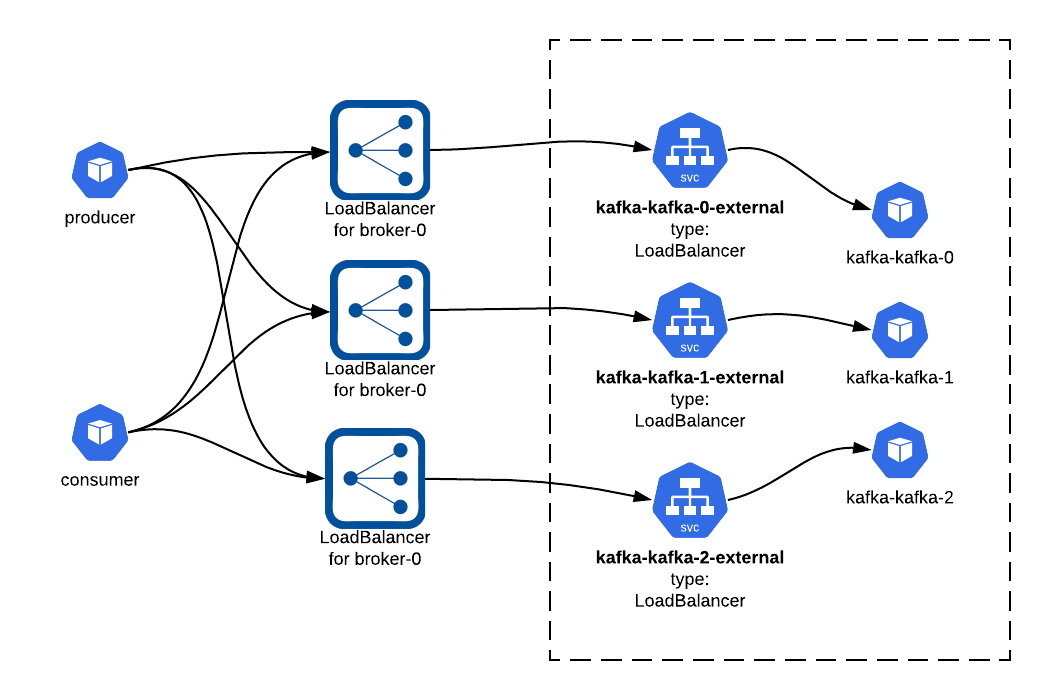
For these Kubernetes Services, KUDO Kafka uses the externalTrafficPolicy:local to avoid any second hop. As each broker gets its own loadbalancer we can avoid the extra hops and get a better network performance.
$ kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kafka-kafka-0-external LoadBalancer 10.0.13.34 aebb0d2f2adda4b22b7d9b0c07a865b8-1700665253.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com 9097:31713/TCP 11s
kafka-kafka-1-external LoadBalancer 10.0.45.151 a8ae206a726b24fed91b82eb9110e0d1-1872607345.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com 9097:30786/TCP 11s
kafka-kafka-2-external LoadBalancer 10.0.32.219 a252e64a36f4443ecbea2fa4c4bf8441-1574422153.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com 9097:32048/TCP 11s
Producers and consumers can connect to aebb0d2f2adda4b22b7d9b0c07a865b8-1700665253.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com:9097,a8ae206a726b24fed91b82eb9110e0d1-1872607345.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com:9097,a252e64a36f4443ecbea2fa4c4bf8441-1574422153.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com:9097 in the above case.
To verify if the server.properties has the correct configuration for the listeners,advertised.listeners and listener.security.protocol.map, users can check the server.properties content in the broker pods. For example for broker 2 you just need to run the following command:
$ kubectl exec -ti kafka-kafka-2 -c k8skafka cat server.properties
[ ... lines removed for clarity ...]
listeners=INTERNAL://0.0.0.0:9095,EXTERNAL_INGRESS://0.0.0.0:9097
advertised.listeners=INTERNAL://kafka-kafka-2.kafka-svc.default.svc.cluster.local:9095,EXTERNAL_INGRESS://a252e64a36f4443ecbea2fa4c4bf8441-1574422153.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com:9097
listener.security.protocol.map=INTERNAL:PLAINTEXT,EXTERNAL_INGRESS:PLAINTEXT
inter.broker.listener.name=INTERNAL
[ ... lines removed for clarity ...]
In the above case we can see that loadbalancer hostname is listed in advertised.listeners and listening on PLAINTEXT protocol.
To have the loadbalancer hostname, KUDO Kafka brokers wait for the loadbalancer hostname or IP address to be assigned. And add the address to the advertised.listeners
# Enabling/Disabling Loadbalancer access in already running KUDO Kafka
KUDO Kafka supports enabling and disabling of the parameter EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER. This allows users to switch on and off the loadbalancers for an already running KUDO Kafka cluster.
To enable the external access via load balancers:
$ kubectl kudo update --instance=kafka-instance \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER=true \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER_TYPE=LoadBalancer
To disable the external access via load balancers:
$ kubectl kudo update --instance=kafka-instance \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER=false
# Nodeports
Exposing the Apache Kafka brokers using the NodePorts Service Type isn't a recommended way for the KUDO Kafka in production. But it can help during development and testing environments, when user isn't looking for an external LoadBalancer service.
The parameter used to configure the external loadbalancers is EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER_TYPE
When set to NodePort it creates one service per broker.
kubectl kudo install kafka --instance=kafka-instance \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER=true \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER_TYPE=NodePort
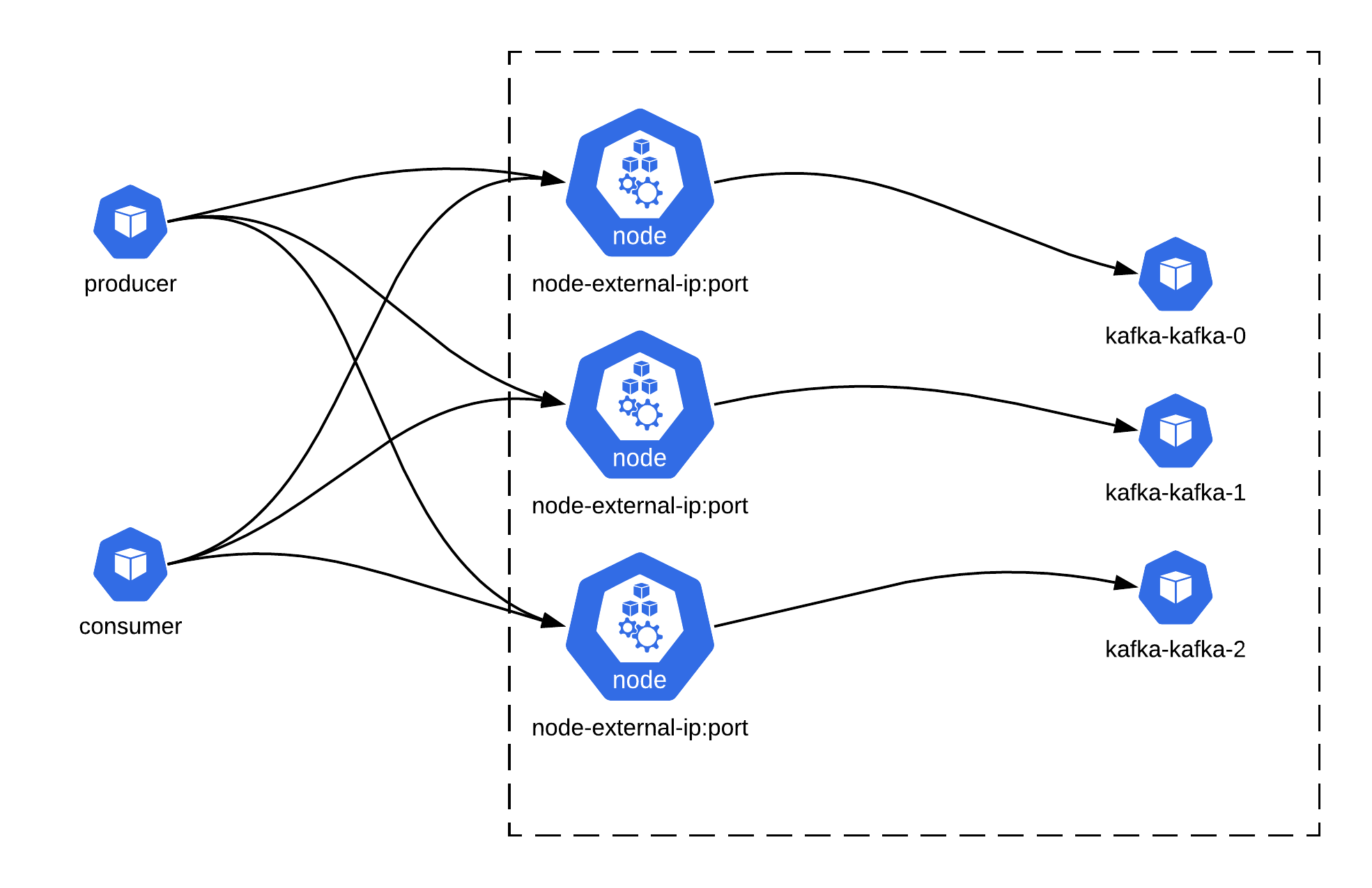
To verify if the NodePorts services are configured correctly, we can check the services created:
> kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kafka-kafka-0-external NodePort 10.0.16.144 <none> 30902:30902/TCP 110s
kafka-kafka-1-external NodePort 10.0.63.204 <none> 30903:30903/TCP 110s
kafka-kafka-2-external NodePort 10.0.11.74 <none> 30904:30904/TCP 110s
In this case we don't have an EXTERNAL-IP and this is expected. To access those brokers externally we would need the nodes external ip addresses to be added to the KUDO Kafka server.properties.
We can verify them by checking the server.properties
> kubectl exec -ti kafka-kafka-2 -c k8skafka cat server.properties
[ ... lines removed for clarity ...]
advertised.listeners=INTERNAL://kafka-kafka-2.kafka-svc.default.svc.cluster.local:9093,EXTERNAL_INGRESS://34.214.27.71:30904
[ ... lines removed for clarity ...]
34.214.27.71 in this case is the node external-ip where the pod is running.
Another way to get the list of all brokers addresses is:
kubectl exec -ti kafka-kafka-0 -c k8skafka cat external.advertised.listeners
kubectl exec -ti kafka-kafka-1 -c k8skafka cat external.advertised.listeners
kubectl exec -ti kafka-kafka-2 -c k8skafka cat external.advertised.listeners
kubectl exec -ti kafka-kafka-1 cat external.advertised.listeners
kubectl exec -ti kafka-kafka-2 cat external.advertised.listeners
That should give an output similar to:
EXTERNAL_INGRESS://34.221.252.205:30902
EXTERNAL_INGRESS://54.202.126.173:30903
EXTERNAL_INGRESS://34.214.27.71:30904
This also explains why using NodePort in production isn't recommended. As in case if any node loss or in case a broker is scheduled to a new node, the external-ip address will be changed. The same case is handled well by the LoadBalancer alternative.
# Enabling/Disabling NodePort access in already running KUDO Kafka
KUDO Kafka supports enabling and disabling of the parameter EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER. This allows users to switch on and off the nodeports access for an already running KUDO Kafka cluster.
To enable the external access via node ports:
kubectl kudo update --instance=kafka-instance \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER=true \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER_TYPE=NodePort
To disable the external access via load balancers:
kubectl kudo update --instance=kafka-instance \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER=false
# Switching access type in running cluster
Due to known kubernetes issue in issues/221 (opens new window) switching the Loadbalancer access to Nodeport access and vice versa, is a two step update
# Switching from Nodeport to Loadbalancer
First disable the external access
kubectl kudo update --instance=kafka-instance \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER=false
Once the plan status is complete, we can enable again with LoadBalancer type
kubectl kudo install kafka --instance=kafka-instance \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER=true \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER_TYPE=LoadBalancer
# Switching from Loadbalancer to Nodeport
First disable the external access
kubectl kudo update --instance=kafka-instance \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER=false
Once the plan status is complete, we can enable again with NodePort type
kubectl kudo install kafka --instance=kafka-instance \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER=true \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER_TYPE=NodePort
# Security
KUDO Kafka Security options plays well with the external access. Enabling Kerberos or TLS authentication methods will modify the required external security protocol map.
# Loadbalancer with TLS encryption enabled
Exposing KUDO Kafka works with the TLS encryption enabled.
kubectl kudo install kafka --instance=kafka-instance \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER=true \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER_TYPE=LoadBalancer \
-p CLIENT_PORT_ENABLED=false \
-p TRANSPORT_ENCRYPTION_ENABLED=true \
-p TLS_SECRET_NAME=kafka-tls
And we can verify that EXTERNAL_INGRESS is using SSL protocol.
> kubectl exec -ti kafka-instance-kafka-2 -c k8skafka cat server.properties
[ ... lines removed for clarity ...]
listeners=INTERNAL://0.0.0.0:9095,EXTERNAL_INGRESS://0.0.0.0:9097
advertised.listeners=INTERNAL://kafka-kafka-2.kafka-svc.default.svc.cluster.local:9095,EXTERNAL_INGRESS://a252e64a36f4443ecbea2fa4c4bf8441-1574422153.us-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com:9097
listener.security.protocol.map=INTERNAL:SSL,EXTERNAL_INGRESS:SSL
inter.broker.listener.name=INTERNAL
[ ... lines removed for clarity ...]
# Nodeport with TLS encryption enabled
Exposing KUDO Kafka works with the TLS encryption enabled.
kubectl kudo install kafka --instance=kafka-instance \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER=true \
-p EXTERNAL_ADVERTISED_LISTENER_TYPE=NodePort \
-p CLIENT_PORT_ENABLED=false \
-p TRANSPORT_ENCRYPTION_ENABLED=true \
-p TLS_SECRET_NAME=kafka-tls
And we can verify that EXTERNAL_INGRESS is using SSL protocol.
> kubectl exec -ti kafka-instance-kafka-2 -c k8skafka cat server.properties
[ ... lines removed for clarity ...]
listeners=INTERNAL://0.0.0.0:9095,EXTERNAL_INGRESS://0.0.0.0:9097
advertised.listeners=INTERNAL://kafka-kafka-2.kafka-svc.default.svc.cluster.local:9095,EXTERNAL_INGRESS://34.214.27.71:30904
listener.security.protocol.map=INTERNAL:SSL,EXTERNAL_INGRESS:SSL
inter.broker.listener.name=INTERNAL
[ ... lines removed for clarity ...]